Deploy microservices using AWS EKS
Part 1
One of the easiest option for deploying and managing Kubernetes on AWS is by using
AWS EKS. This is an exercise of deploying
a system composed of 2 microservices using AWS EKS, how to manage that cluster and how to test this deployment.
Install and configure eksctl
Push docker instance to AWS ECR
Using eksctl

Then you can delete the cluster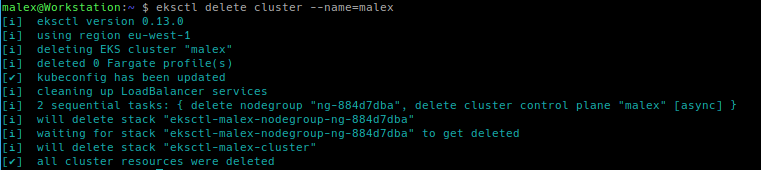 Steps to deploy cluster:
Steps to deploy cluster:
In order to do this I will use a very simple service that is exposing some endpoints. The git repository for this service can be found here.
ServicesInstall and configure eksctl
Push docker instance to AWS ECR
Using eksctl
Services
We will have the same service deployed twice. The service exposes following endpoints:- GET /v1/health - endpoint that we will use to verify that service is healthy. It will also return the name of service and up time.
- GET /v1/reports/simple - endpoint that we will return some data that is configured in the environment variables of the service.
- GET /v1/reports/complete - endpoint that we will return some data that is configured in the environment variables of the service. It will also request GET /v1/reports/simple from the second service, it will concatenate the data and the return it. This endpoint can then be used to fully test the microservice system
- PORT - port where service will listen for requests. (Required)
- NAME - service name. (Required)
- DATA - a simple sting that will be returned in the reports endpoints. (Required)
- NEXT - Next service name. (Optional). If not set then GET /v1/reports/complete will return just the own service data concatenated with string 'N/A'
Install and configure eksctl
For this exercise I used eksctl client - Official CLI for Amazon EKS.- First install eksctl as explained on documentation
- Install and configure AWS CLI sh
- Verify aws cli is configured correctly sh
$ aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]: A....
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: 8...
Default region name [None]: eu-west-1
Default output format [None]: json
$ aws s3 ls
2016-10-19 12:43:52 .....
Push docker instance to AWS ECR
We need a place to store our docker images. AWS ECR is perfect for this and you can find bellow the steps you need to follow in order to push our service Docker image to ECR.- Get AWS password sh
- Docker login sh
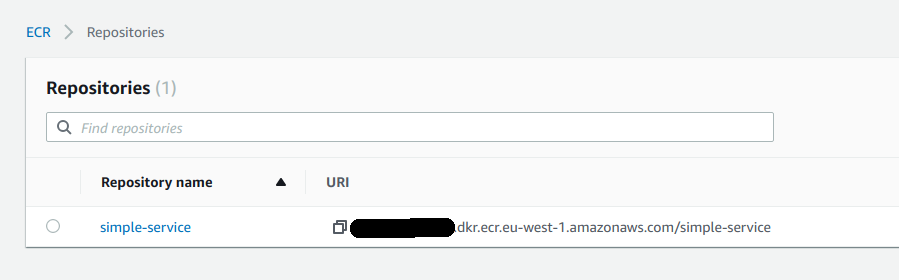
- Create ECR repository sh
- Create docker image for simple service sh
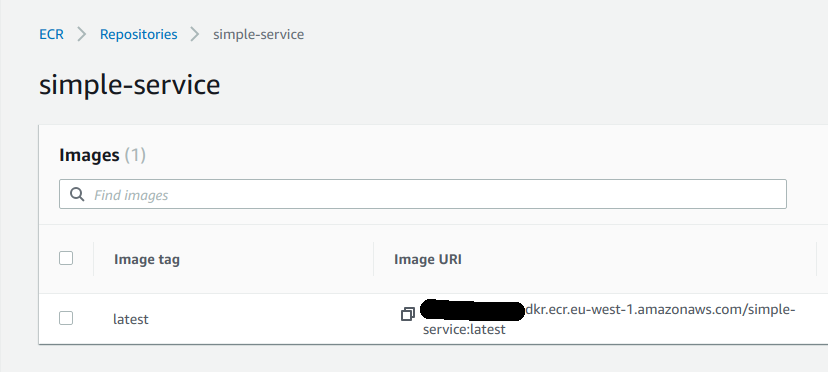
- Tag image and push to ECR sh
$ aws ecr get-login-password --region eu-west-1
eyJwYXlsb2FkIjoibkN4MlVzUm5kUUxTYk9WR3l0WjJwRmdyU0dheUZ0b1YyWlRRbm.....
$ docker login -u AWS -p eyJwYXlsb2 https://{your_aws_account}.dkr.ecr.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com
.....
Login Succeeded
$ aws ecr create-repository --repository-name simple-service
{
"repository": {
"repositoryArn": "arn:aws:ecr:eu-west-1:{aws_account_id}:repository/simple-service",
"registryId": ".....",
"repositoryName": "simple-service",
"repositoryUri": "{aws_account_id}.dkr.ecr.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/simple-service",
"imageTagMutability": "MUTABLE",
"imageScanningConfiguration": {
"scanOnPush": false
}
}
}
$ docker build -t simple-service .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 69.1MB
Step 1/8 : FROM node:8.14.0-alpine
........
Successfully built ddddcb6941de
Successfully tagged simple-service:latest
$ docker tag simple-service:latest {aws_account_id}.dkr.ecr.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/simple-service
$ docker push {aws_account_id}.dkr.ecr.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/simple-service:latest
The push refers to repository [{aws_account_id}.dkr.ecr.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/simple-service]
0fd5e3eeb047: Pushed
d26ee7e7e5a7: Pushed
bd180bd6f1d8: Pushed
4964afdee176: Pushed
0c1c3171d8c7: Pushed
2283a7db78c9: Pushed
df64d3292fd6: Pushed
latest: digest: sha256:e112e9e3a6cf81d28ae97f830eea52c01354449f59e9ad7044b6bea44788a298 size: 1789
Using eksctl
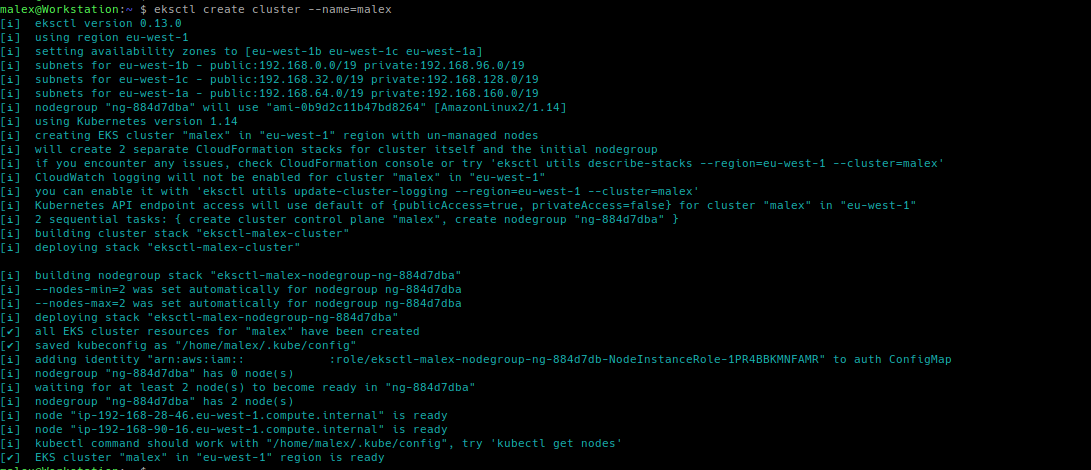
A simple test for eksctl is to create a cluster using the default configuration:

Then you can delete the cluster
 Steps to deploy cluster:
Steps to deploy cluster:
- Create cluster using the configuration file. sh
- Make sure aws-iam-authenticator is also installed on local machine.
- Now we can start using kubectl, everything is configured correctly. sh
- Create deployment/service and pod for service #1 sh
- Create deployment/service and pod for service #2 sh
- We can ssh to our node and try some curl commands sh
- external ip for our node is 54.77.67.122
- ip:port to access service for simple-service1 is 192.168.38.224:30000
- Kubernetes cluster deployed and managed on AWS EKS
- service docker images stored in AWS ECR repository
- Two deployments, each with replica of one pod
- Pods can communicate using the kubernetes service discovery
$ eksctl create cluster -f cluster.yaml
[ℹ] eksctl version 0.13.0
[ℹ] using region eu-north-1
[ℹ] setting availability zones to [eu-north-1c eu-north-1b eu-north-1a]
.....
using:
cluster.yaml
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: malex
region: eu-west-1
nodeGroups:
- name: ng-1
instanceType: m5.large
desiredCapacity: 1
ssh:
allow: true
$ kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
ip-192-168-42-23.eu-west-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 8m17s v1.14.8-eks-b8860f 192.168.42.23 18.202.253.46 Amazon Linux 2 4.14.154-128.181.amzn2.x86_64 docker://18.9.9
$ kubectl create -f deployment_service1.yml
using:
deployment_service1.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: simple-service1
labels:
app: simple-service1
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 30000
targetPort: 30000
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: simple-service1
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: simple-service1
labels:
app: simple-service1
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: simple-service1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: simple-service1
spec:
containers:
- name: simple1
image: 210758531925.dkr.ecr.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/simple-service:latest
ports:
- name: http-port
containerPort: 30000
protocol: TCP
env:
- name: SERVICE_PORT
value: "30000"
- name: SERVICE_HOST
value: "0.0.0.0"
- name: NODE_ENV
value: "development"
- name: NEXT
value: "simple-service2"
- name: PROJECT_NAME
value: "service1"
- name: DATA
value: "Dummy data from project 1"
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /v1/health
port: http-port
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 30
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /v1/health
port: http-port
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 30
$ kubectl create -f deployment_service2.yml
using:
deployment_service2.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: simple-service2
labels:
app: simple-service2
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 30000
targetPort: 30000
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: simple-service2
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: simple-service2
labels:
app: simple-service2
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: simple-service2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: simple-service2
spec:
containers:
- name: simple2
image: 210758531925.dkr.ecr.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/simple-service:latest
ports:
- name: http-port
containerPort: 30000
protocol: TCP
env:
- name: SERVICE_PORT
value: "30000"
- name: SERVICE_HOST
value: "0.0.0.0"
- name: NODE_ENV
value: "development"
- name: PROJECT_NAME
value: "service2"
- name: DATA
value: "Dummy data from project 2"
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /v1/health
port: http-port
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 30
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /v1/health
port: http-port
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 30
$ kubectl get service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.100.0.1 443/TCP 55m
simple-service1 NodePort 10.100.255.92 30000:32698/TCP 37m
simple-service2 NodePort 10.100.251.108 30000:30788/TCP 29m
$ kubectl describe service simple-service1
Name: simple-service1
Namespace: default
Labels: app=simple-service1
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"app":"simple-service1"},"name":"simple-service1","namespace":"default"},"sp...
Selector: app=simple-service1
Type: NodePort
IP: 10.100.255.92
Port: 30000/TCP
TargetPort: 30000/TCP
NodePort: 32698/TCP
Endpoints: 192.168.38.224:30000
Session Affinity: None
External Traffic Policy: Cluster
Events:
$ kubectl get node -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
ip-192-168-44-42.eu-west-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 46m v1.14.8-eks-b8860f 192.168.44.42 54.77.67.122 Amazon Linux 2 4.14.154-128.181.amzn2.x86_64 docker://18.9.9
from these commands we know now that:
$ ssh ec2-user@54.77.67.122
....
$ docker ps
.....
$ curl 192.168.38.224:30000/v1/simple
{"data":"Dummy data from project 1"}
$ curl 192.168.38.224:30000/v1/complete
{"data":"Dummy data from project 1, {\"data\":\"Dummy data from project 2\"}"}
So until now we have: